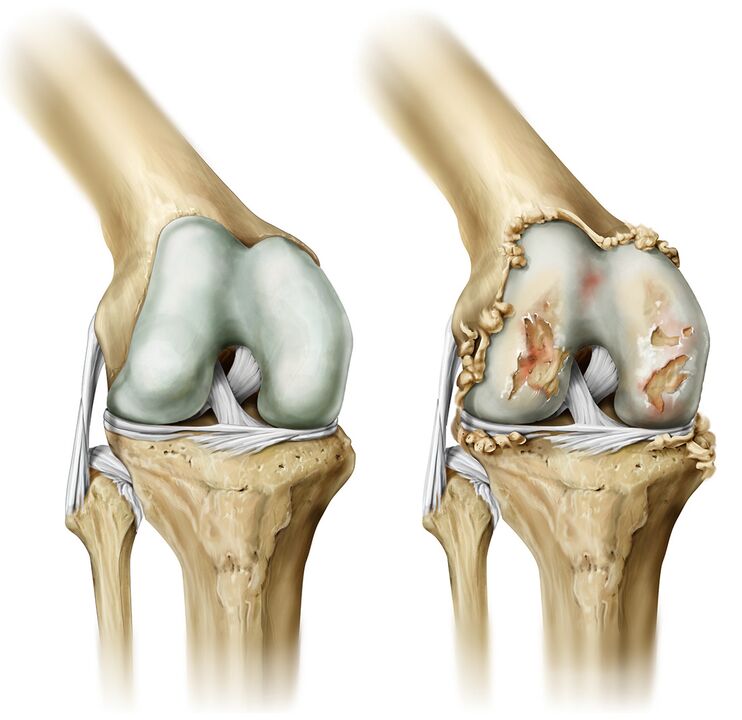
Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease characterized by the development of degenerative changes in articular cartilage, resulting in deformed bone tissue. The big toe, hip, and knee joints are most commonly affected.
Symptoms of the disease
- The first clinical symptom of arthropathy is pain in the affected joint with excessive exertion. Pain may occur with movement. As the disease progresses, joint pain bothers the patient even at rest and causes insomnia.
- Crunching the joints. Due to the destruction of cartilage, bone friction occurs, when moving in the joint, you will hear a clicking and crunching sound. As the disease progresses, the crackling sounds increase.
- Reduced mobility. If the joint is damaged, movement in the joint is limited, with severe joint conditions, the patient has stiffness in the limbs in the morning.
- Joint deformity. Without adequate and timely treatment, the joint will be deformed and change its appearance.
- With exacerbation of the inflammatory process, the patient experiences decreased sensitivity of the toes and numbness of the fingertips.
Cause of disease
The main reason for the development of joint disease is the growth of the cartilage layer between the joint and the bone. The contributing factors are:
- Intense physical activity;
- Joint damage;
- Frequent broken bones
- Wear tight shoes or high heels
- Congenital geography.
Diagnose
The primary method for diagnosing arthropathy is a carefully collected patient history (occupational history).
Diagnosis is made on the basis of patient examination and additional studies, including joint radiography, arthroscopy, ultrasound, MRI, and computed tomography.
- Supersonic. This research method is reliable and harmless. Since ultrasound diagnosis refers to noninvasive methods, this study has no contraindications. With the help of ultrasound, it is possible to diagnose thinning of the cartilage tissue, degenerative changes in the articular cartilage, thickening of the articular membranes, the presence of fluid in the joint cavity. This research allows you to choose exactly a treatment for joint disease.
- MRI and computed tomography. With the help of computed tomography and MRI, it is possible to evaluate the condition of the joints: the thickness of the cartilage, the presence of erosions or cysts in the bone tissue, to determine the amount of fluid in the joint.
- Arthroscopy. This study is done more often to determine the cause of the development of joint disease.
Complications
Without prompt medical care, joint disease can progress and threaten complications such as:
- Inflammation of tissues around joints;
- Limited mobility of the affected joints;
- Degenerative changes in the hip joint;
- Change the shape of the joints.
Cure
Treatment is indicated for the patient depending on the extent of joint damage. Treatment for dry joints begins with pain relief.
In parallel with pain relievers, patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs. In addition to drug treatment, the patient must undergo physical therapy.
Massaging the affected limbs after the acute form of the inflammatory process goes into remission can relieve pain, normalize joint mobility and relieve muscle spasms.
Physical therapy exercises are indicated to reduce stiffness in the muscles, warm up and improve the patient's general condition. Exercise helps maintain correct posture and regular gait.
Convalescent treatment is indicated during the stable remission of the disease. Mud baths, applications, and other procedures help restore joint mobility and relieve pain.
If conservative treatments do not bring the expected results, the patient is indicated for joint replacement surgery. Endoprosthes are made from a material that is not eliminated by the human body. They allow you to fully restore the physiological functions of the affected joint.
Unique treatment: radiofrequency ablation and disruption of the integrity of the method by disrupting the integrity of the nerve causing pain.
Risk group
The risk group includes people who:
- Overweight;
- Varicose veins;
- Athletes;
- Pianist;
- Programmer.
Preventive
Prevention of joint disease is as follows:
- Good nutrition;
- Prevention of injuries and fractures;
- Limiting the load on joints with a genetic predisposition;
- Body weight control;
- Wear comfortable shoes.
Diet and lifestyle
With genetic factors in the development of rheumatic diseases, as well as during exacerbations of the disease, it is necessary to adjust the diet. It is recommended to supplement the diet with sea fish (sardines, salmon, tuna), fresh vegetables and fruits, whole grains. Limit baked goods, fatty meats, chocolate, and alcohol.
Should spend a lot of time in contact with fresh air and do not let bones and joints increase movement.





































