Spinal tumor is a degenerative-dystrophic lesion of the disc, vertebral body, ligamentous apparatus, in which the bone and cartilage tissue of the neck, chest and lumbar spine are destroyed.
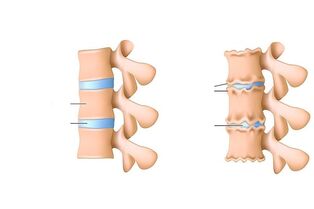
Pathology affects the entire movement of the spine, disc, both vertebral bodies and neighboring nerve and muscle structures. This disease is often called the "disease of civilization", and is related to sitting up straight postures and stressing on the daily spine.
The main cause of degenerative spine disease is micro-injury during exercise, unhealthy diet, sedentary lifestyle and even genetic factors. If the disease is more advanced, the disc and its adjacent structures are affected first. A change in the central part of the disc leads to a loss of the pulse-absorbing properties of the vertebra, thus forming cracks and thinning in the fibrous sac.
American statisticians said that the first reason why people under 45 years of age restrict activities is pain in the spine and neck spine. The majority of urban residents, drivers, who spend most of their time in a sitting position, reloading their spine, are at risk.
Osteochondrosis is the cause of more than 70% of back pain cases. The risk of disease increases with age.
Etiology and pathogenesis of myeloma
Fibroids have a long pathogenesis (from several months to dozens of years). It depends on the factors that influence the development of the disease.
Risk Factors:
- Age. The elderly (over 60) are at risk. In people under 35 years old, the disease is rare. As a result of age-related changes, a violation occurs in the human hormonal background, causing muscle tissue and blood vessel walls to become more spongy, which means more damage. This causes metabolic disorder, overloading the disc.
- Autoimmune diseases can take cartilage tissue as foreign and begin to destroy it.
- Injury to the spine. This is one of the main reasons for the development of osteonecrosis in young people. It is believed that more than half of people with spinal cord injuries as a child develop spinal necrosis in old age.
- Overweight, reducing disc wear. Cartilage disc acts as a kind of shock absorber for the spine, ensuring its mobility during physical activity, walking, running, etc. v. , and protects bone tissue from destruction and the appearance of minor cracks. The severity of the excess weight makes the load even more powerful, increasing the speed at which cartilage discs are destroyed.
- Flat feet.
- Genetic disposition.
- Diseases of the endocrine system, causing metabolic disorders, thereby negatively affecting the state of cartilage tissue.
The bone tumor can be in a "inactive state" for a long time. Many patients, when learning about the disease, experience intense pain, when dystrophy in cartilage tissue damages nerve roots.
There are such stages in the pathogenesis of spinal necrosis:
- Violation of blood circulation in the intervertebral disc and neighboring structures.
- Hormonal and metabolic disorders in the body and especially the disc.
- Degenerative processes of the myeloid nucleus. At this stage, the structure of the disc changes - the core decreases, the disc itself becomes thinner, the load on the annular fibers increases, resulting in more stratification, small cracks and sometimesbroken.
- protrusion of the disc - protrusion of the tissue of the disc, usually toward the spinal canal, compresses it, causing severe pain.
- Disc herniation. The progression of protrusion leads to destruction of ligaments, a change in the height and shape of the disc, thereby causing the formation of a hernia.
- Compression of the lens artery.
- Chronic anemia supplied to the spinal cord.
Symptoms of spinal necrosis
As osteoporosis develops, pathologies appear in the disc and within the cartilage itself, which then overlap and can cause the appearance of a herniated disc.
Symptoms may be general and specific, characteristic of pathological changes in the cartilage, disc, and neighboring tissues.
The first sign of osteonecrosis should be called back pain, numbness of the vertebrae, limited movement, increased pain during exertion.
Specific symptoms of osteonecrosis:
- Fibroids of the cervix are characterized by impaired blood circulation, causing dizziness, pain and tinnitus, headache. The brain is poorly supplied with oxygen and nutrients, so a person experiences a state of stress.
- Tumor of the thoracic region, often accompanied by intercostal neuralgia. There is pain in the chest and ribs.
- Lumbar spinal cord tumors stimulate the development of lumbar pains, sciatica (sciatica) and lumbar sciatica. In sciatica, the sciatica is affected, pain and low blood pressure in the buttocks, as well as a drop in blood pressure in the calf.
Symptoms of cervical bone necrosis:
- Cervical pain - pain in the cervical spine. The nature of the pain is varied (dull, sharp pain, worse when tilting the head and body, when coughing), depending on what factors affect this part of the spine.
- Cervicobrachialgia - pain in the spine of the neck, spreading down the arm, numbness.
- Degenerative shoulder joint disease and posterior arthritis - pain in the shoulder joint, clavicle, restriction of hand movement from top to bottom.
- Spinal degeneration - elbow joint pain, limited movement.
- Spinal artery syndrome - also known as cervical migraine, headache and cervical headache, nausea, sometimes vomiting, impaired coordination - faintness when walking, Tinnitus.
One of the most common signs of fibroids is impaired blood circulation, leading to frequent dizziness, fainting, and headaches.
Symptoms of breast bone necrosis:
- Angina - chest pain, pain with immobility (manifested by long sitting, at night), exacerbated by physical activity, deep breathing, cough.
- Heart syndrome.
- Posterior chest wall syndrome - pain in the shoulder blade area, pain sensation depending on the position of the body.
- Anterior squamous muscle syndrome.
- Conjunctivitis - pain in the chest half.
- Exacerbating intercostal pain.
Symptoms of lumbar necrosis:
- Lumbodynia - low back pain, low back pain. The sick person feels uncomfortable when trying to sit or stand. Pain increases with physical activity, coughing, breathing deeply, bending over.
- Lumboischialgia - pain in the lower back, spreading down the legs. Paresthesia, leg numbness, muscle spasticity and joint pain may be present.
- Vascular syndromes - they begin with compression of blood vessels, not accompanied by pain, with muscle weakness, cone syndrome - weakness of both legs, dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
The symptoms of osteonecrosis of the lumbar spine vary. This part of the spine is loaded with more load than the others.
Diagnosis of spinal cord tumors
When you experience back pain first, you should see a doctor to determine the source of the pain. Bone tumors are difficult to diagnose, as the pain can be caused by other conditions not related to the spine. The patient will need to consult a number of specialist physicians: neurologists, first of all, orthopedic physicians, spine specialists.
Methods for diagnosing bone necrosis:
- X-ray. It is done to accurately determine the height of the disc or changes in the structure of the vertebrae, changes in the diameter of the holes between the vertebrae. X-rays are usually done in two positions - lying on your back and lying on your side. Two different image projections help to more accurately identify the presence of the pathology. Sometimes X-rays are taken with the lower jaw down.
- MRI and CT. MRI results are considered to be more accurate and help to quickly locate the segments affected by the pathology, the presence or absence of disc herniation and root compression.
- Test: a blood test to determine the level of calcium in the blood and the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation. Laboratory tests are prescribed by those who first, more recently, on the basis of these results, doctors direct them to diagnose hardware.
It is important to differentiate osteonecrosis of the spine from some other diseases with a similar clinical picture, e. g. a tumor on the spine has a cancerous nature, which violates tissue integritycartilage, inflammation, intermittent obstruction, cyst formation on internal organs, urolithiasis, gastritis, pyelonephritis, gastric ulcer, angina, nervous system disorders. For this purpose, studies of the digestive system, nervous system and blood circulation may be prescribed. The following diagnostic methods are used - electrocardiogram, ultrasound, electroencephalography, endoscopy (digestive organs).
Complications of osteonecrosis
Usually the course of this disease is accompanied by neurological complications:
Phase- . Complications from bulging eyes - sharp pain during the scan. Stage
- . Root inflammation, characterized by pain syndromes and other symptoms, depends on the site of root tissue inflammation. Stage
- . Pathology of the roots and spinal nerves, the presence of disc herniation. Usually, muscle paralysis occurs, leading to a total paralysis of the body. Stage
- . Violation of blood circulation and blood supply to the entire spinal cord. Symptoms: persistent severe back pain, paralysis of some muscle groups, ischemic stroke of the spinal cord.
Treatment of spinal necrosis
The process of treating any type of bone necrosis pursues one goal - relieving pain, preventing destruction and deformation of spinal tissues. Treatment can be conservative or surgical. Type and method of treatment are assigned individually for each patient, based on diagnosis (stage, type of disease, general health of the patient).
In the acute phase of the pain syndrome, it is recommended to relax and rest, it is possible to prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs (dicloberl, voltaren), injections of antispasmodic mixes, vitamin B, rubbing preparations - dipping rileaf, larkspur, v. v. , can be prescribed when pain syndrome subsides. physical education and physiotherapy (diadynamic electric current, electrophoresis, magnetotherapy).
Conservative treatment takes about two months. In addition to the listed treatments, massage, manual therapy, reflexology, and extract therapies can also be used. The results of conservative treatment are directly dependent on patient persistence and diligence.
There is also a surgical treatment, to be used in cases of disc herniation over six months, squeezing the roots of the spinal cord due to narrowed spacing between the vertebrae. The principle of surgical treatment is to remove a deformed disc. The rehabilitation time after surgery is about six months. Rehabilitation includes exercise therapy, physical therapy, and vitamin intake.
Prevention of osteoporosis includes combating risk factors - keeping an active lifestyle, playing sports, getting proper nutrition, using special belts and belts when resting your back, sleeping on a mattressand orthopedic pillows, avoiding hypothermia and trauma.





































