Joint deformity (osteoarthritis) is a progressive disease that leads to dystrophy and degeneration of the joint surface and damage to cartilage, resulting in complete destruction of the joint area.
Usually, deforming arthropathy is detected in old age, when comorbidities and factors are present, it is often detected on examination, but not clinically.
Joint deformity is the most common and frequent joint disease. It occurs in 70% of all joint diseases.
Reason
The exact cause of joint deformity remains unknown, but several factors have been identified that reliably increase its likelihood of development. First of all, there are general aging phenomena of the body and the phenomenon of tissue dystrophy, changes in cartilage and joint capsule.
Factors that influence the development of osteoarthritis can be divided into:
- extrinsic - includes overloading of joints (eg, from lifting weights), permanent trauma, occupational effects, hypothermia of the joints,
- internal - this is the influence of genetics with excessive stretching of the ligaments and laxity of the joints, dysfunction of the ovaries and changes in bacteria in women, vascular accidents, deteriorationblood circulation in cartilage tissues, obesity.
Joint deformity, as one of the symptoms, can be caused by alcoholism or myoedema, acromegaly or hormone therapy, with congenital hip dislocation, Marfan syndrome (a genetic disease characterized by mobilityjoints are overextended and the tubules are elongated). joint stiffness)
Stages of development
In the development of deforming arthropathy, there are several successive stages that frequently alternate with each other:
- water loss of cartilage, leading to thinning and dryness,
- formation of defects and cracks in the cartilage,
- destruction of cartilage with simultaneous sharp narrowing of the joint space,
- the disappearance of cartilage from the bone border,
- compensatory compression of the ends of bones, without a cartilaginous surface,
- disorders of the joints with dislocations, fractures and dysfunction of the limbs.
Symptoms of joint deformity
First of all, the main manifestation of deformed joint disease is
- pain inside the joint, worse after exercise or at night,
- individual joints are affected,
- asymmetrically affected joints,
- at the same time without the usual signs of joint damage,
- No fever
- no strong redness of the joints,
- There was no change in the analysis.
This process usually occurs in the ankle, knee, hip, or intervertebral joints.
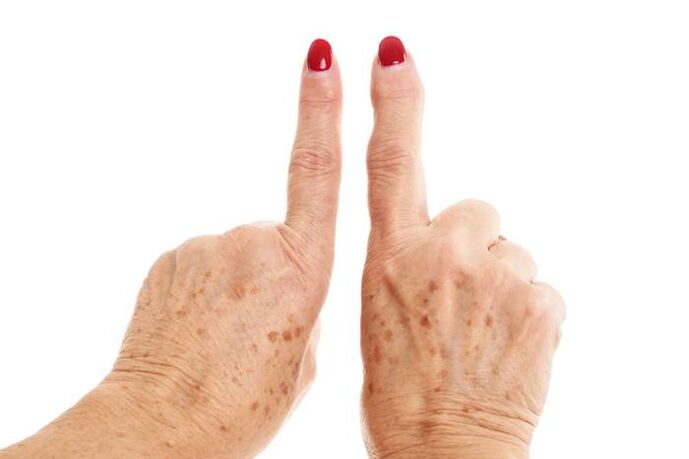
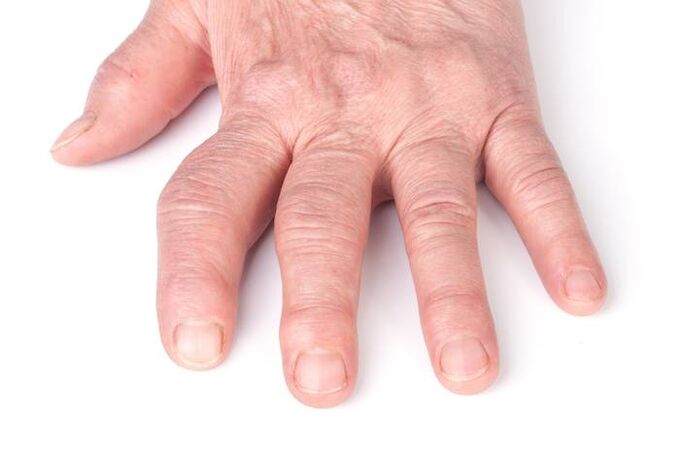

If the disease progresses to the point of destroying cartilage, the joint becomes blocked causing pain, when walking, there is severe pain that makes the legs unable to move and must stop. This is because pieces of cartilage or small pieces of bone ("rat" in the joint) get into the joint cavity.
In the joint area above the joint, there are nodules, very hard, while the joint is not deformed much, the muscle is not atrophied and there is no ankylosing phenomenon (joint immobility).
Inside the joints, when moving, there will be a crunching sound due to the friction of uneven surfaces against each other.
Pain and limited mobility can cause spasticity (muscle spasm), shortening the leg or arm.
Joint deformity in its manifestations is similar to other forms of arthritis, first of all it must be distinguished from rheumatoid arthritis.
Diagnose
There are no typical criteria for the diagnosis of joint deformity; superficially recognizable only by the nodules on the phalanges of the fingers. Osteoarthritis is suspected when:
- typical joint damage,
- long-term development of the disease over many years,
- elderly patients.
The basis of the diagnosis is radiological data arising even before the period of clinical manifestations and pain syndrome.
Narrowing of the joint space, changes due to flatness and surface deformation of the joint, instability in the joint area with dislocations and dislocations, marginal bone growth, fibrosis (increased biliarybone degree).
As this process progresses, bone spurs and condyles are exposed, and the joint space can become wedge-shaped.
The study was complemented by arthroscopy, a blood test that shows no markers of inflammation.
It is necessary to conduct a study of peristaltic fluid.
Treatment of deformed joints
The treatment is carried out by traumatologists and orthopedists.
Treatments for joint deformities depend on how involved the joints are in the process, as well as the duration of the injury and the presence of pain.
First of all, conservative therapy is used.
- reduce stress on joints,
- weight loss,
- the use of metabolites - a course of aloe or vitreous is injected intramuscularly in the course,
- Using drugs that stimulate cartilage restoration in the form of intramuscular injections in the course of treatment.
Additional treatment:
- the use of quinolones,
- anti-inflammatory therapy.
If there is inflammation in the joint, a course of intra-articular hormones will be indicated.
A combination of massage therapies, physiotherapy effects, mud therapy, thermal effects is also used. The spa treatment is very helpful.
In advanced cases, surgical treatment helps - arthroplasty. In the future, physical therapy exercises will be applied to joint removal, weight loss, walking with the support of a cane or crutches.
Forecast
Joint deformities that do not require necessary treatment have a slow but steady progression. Leads to significant disability and dysfunction of the joints, disorders of movement. Therefore, when the first signs of osteoarthritis appear, aggressive treatment is indicated, lasting for 1-2 months.





































