
What do programmers, accountants and artists have in common?Cervical spine degeneration!This disease significantly impairs a person's quality of life and performance.Prolonged static or uncomfortable head position leads to changes in the bone tissue of the cervical vertebrae.Many patients with cervical spondylosis complain mainly of pain, dizziness, and limited movement in the neck.But no less frequent are pain or numbness in the chest, arms, various parts of the head, tinnitus, nausea and the so-called cervical syndrome.
Other manifestations of cervical spondylosis (symptoms) may also occur: brittleness and pain in the neck when turning or tilting the head, tingling in the arms or legs, burning between the shoulder blades, dizziness and even fainting when turning the head suddenly, decreased vision and hearing loss, sometimes persistent pain in the heart, feeling of weakness and fatigue.Osteonecrosis of the spine is associated with degenerative-dystrophic damage to the intervertebral discs, which cause loss of elasticity and possible destruction.Normally, salt will deposit in the area of the intervertebral discs, forming bone growth, causing pain due to nerve root compression.
What is osteonecrosis?
There are different forms of this disease:
- Cervix;
- neck and chest;
- Lumbar sacral.
Let's look at cervical osteonecrosis.
Cervical spine degeneration– a progressive disease that represents a degenerative-dystrophic disorder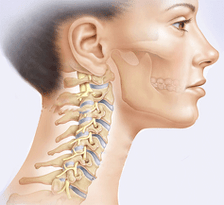 intervertebral disc of the cervical spine.
intervertebral disc of the cervical spine.
Cervical osteonecrosis is the most dangerous disease.The cervical spine consists of seven discs and is the most mobile part of the spine, providing the ability to tilt and turn the head.He has a relatively weak muscle corset.At the same time, the instability of the cervical spine combined with constant physical activity (the need to support the head, control rotation and bending) explains the high susceptibility of this part of the spine to both injuries and degenerative changes, essentially osteoarthritis.
The small neck area contains many nerve tubes and blood vessels that supply the brain.In the neck area, the vertebrae fit tighter together.So even with
 A small change in one of the vertebrae can cause compression or displacement of nerves and blood vessels.
A small change in one of the vertebrae can cause compression or displacement of nerves and blood vessels.Due to disorders of cerebral circulation, migraines, vegetative dystonia and hypertension, problems with the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, hearing, vision and coordination occur.In its advanced form, cervical spondylosis can lead to vertebral artery syndrome.The vertebral artery supplies blood to the medulla and cerebellum.When the artery is compressed, ischemia of the brain and spinal cord can develop and a spinal stroke can occur.
Cervical spondylosis leads to nerve root damage - formation of tumors on the vertebrae, partial or complete loss of mobility.The most serious consequence of cervical spondylosis is spinal cord compression, which can cause death.Serious consequences can be avoided if the disease is treated promptly.
The main reasons for the early development of cervical spondylosis:
- Flat feet;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Work that involves lifting heavy objects;
- Genetic predisposition (heredity);
- Metabolic disorders in the body, infections, poisoning;
- Overweight;
- Poor nutrition (lack of trace elements, vitamins and fluids);
- Spinal injuries (bruises, fractures);
- Bad posture, scoliosis;
- Instability of spinal segments;
- Work involves frequent changes in body position (rotation, flexion, extension, jerking);
- Staying for a long time in an uncomfortable position when standing, sitting, lying, when lifting and carrying heavy objects, when performing any work that puts stress on the cervical spine and the entire spine;
- Excessive physical activity with an underdeveloped musculoskeletal system;
- Nervous tension and stress;
- Hypothermia;
- Using the wrong pillow when sleeping.
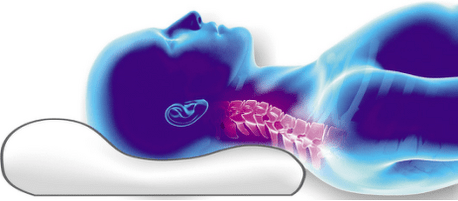
Why do you need an orthopedic pillow?

An orthopedic pillow for cervical spondylosis is an indispensable thing, as it allows you to achieve complete relaxation of muscle fibers and avoid compression of blood vessels leading to poor circulation.What should an orthopedic pillow look like?Here are its signs:
- The presence of an anatomical shape (roller or roller, a special depression for the shoulder);
- Elasticity of the material;
- Ability to maintain its shape for a long time;
- The material is safe and hypoallergenic.
Let me explain a bit.
- The neck cushion carefully cradles the head and provides adequate support for the cervical vertebrae.Orthopedic pillows have 2 supports of different heights, used for
 Different body positions, suitable for sleeping on back and side.A team of experts has developed a pillow design with grooves (one or two) under the shoulders to properly support the neck and head when sleeping - especially on the side.The shoulder concave shape helps you find a comfortable position and keeps your spine straight.
Different body positions, suitable for sleeping on back and side.A team of experts has developed a pillow design with grooves (one or two) under the shoulders to properly support the neck and head when sleeping - especially on the side.The shoulder concave shape helps you find a comfortable position and keeps your spine straight. - The elasticity of a material is the ability of a material to regain its shape after pressure.
- It is very important that after sleeping on the pillow it does not lose its shape, otherwise how will it "work"?
- Well, there is nothing to explain about the material being safe and hypoallergenic.Nose contact with the pillow should not inhale anything harsh, chemical or harmful to health.Otherwise, at best we will wake up with a headache, and at worst we will be miserable.
 allergy.By the way, house mites, the main household allergen, love to live in ordinary down and feather pillows.
allergy.By the way, house mites, the main household allergen, love to live in ordinary down and feather pillows.
The first three properties are possessed by two materials: polyurethane foam and latex.Latex is well known to many people from rubber gloves, condoms, and rubber nipples.It is obtained from the sap of the Hevea rubber tree, which grows in several places.So, orthopedic pillows made of natural latex found on our market are much more expensive than polyurethane foam pillows.In addition, latex can cause allergies.That's why we love polyurethane foam pillows with a “memory effect”.They have all four of these properties and, importantly, are cheaper than latex.
Prevent osteoarthritis
Recommendation:
- Sleep on an orthopedic foam pillow (pillow choice is individual);
- Take a hot bath for 10 minutes;
- Swimming, yoga, walking more;
- Avoid sudden head movements;
- Avoid heavy loads on the spine or significantly reduce the number of activities such as: running, jumping, strenuous exercise in the gym;
- When working at the computer, take a 5-minute break every hour.During breaks, walk, tilting your head and torso in different directions;
- When sitting at a desk or computer, keep your head and back straight;
- Choose chairs and armchairs with spinal support (orthopedic chair cushions with a square or ring shape under the back, which significantly reduce the load on the spine, can also save the day).
Exercise for osteoarthritis
These exercises will help both with existing osteoarthritis in the cervical spine and as a preventive measure.For preventive purposes, exercises for cervical spondylosis can be performed in the evening at home, but it is better to use short breaks from work for this (this is recommended for people with sedentary work).Exercise to treat cervical spondylosis does not take much time but gives positive results and is quite quick.
Exercise 1.Sit up straight, tilt your head back and try to touch your right ear with your right shoulder, then return to the starting position.The exercise is performed slowly and rhythmically, without tension in the muscles.Do five repetitions on each side.
Exercise 2.Sit up straight, face forward, chin slightly raised.Slowly and gently turn your head to the right - as much as possible.Return to the starting position and turn left similarly.Repeat 5 times in each direction.
Exercise 3.Place your palm on your forehead and press your head there, at the same time your palm should remain in position, that is, resist pressure.When pressing with your head, you need to tense your neck muscles.Slowly count to 5 and relax.Repeat 3 times.
Exercise 4.The exercise is similar to exercise 3, just place your palm (or two palms) behind your head and press on the palm.Must maintain tension, counting to 5. Repeat 3 times.
Exercise 5.The exercise is similar to exercise 3, but in this case, the right palm should be placed on the right temple and the head should be placed against the palm.Must maintain tension, counting to 5. Repeat 3 times.Then do the same, placing the left palm on the left temple - repeat 3 times.
Exercise 6.Sit up straight, tilt your head slightly back and then slowly, with a tense posture, as if overcoming resistance, lower your head, pressing your chin to your chest.Repeat 5 times.
Exercise 7.Sit up straight, lower your head and slowly turn your head to the right and left - each direction 5 times.At the same time, the head remains bowed.
Gymnastics for cervical spondylosis should not include turning the head without the support of the hands, especially during times of neck tension and pain.
In severe cases, it is necessary to consult an orthopedist.You may need prescription medications, massage therapy, and physical therapy.





































